VoIP Network Fundamentals
A fast, visual guide to the network concepts that make or break call quality.
Quick Navigation
QoS (Quality of Service)
QoS prioritizes voice packets over bulk data so calls stay clear even when the network is busy.
- Set WAN upload/download shapers to ~85-90% of real speeds to keep the router in control.
- Reserve voice bandwidth based on max concurrent calls + ~20% overhead.
- Typical starting point: allocate 20-30% of the uplink for VoIP, then adjust.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
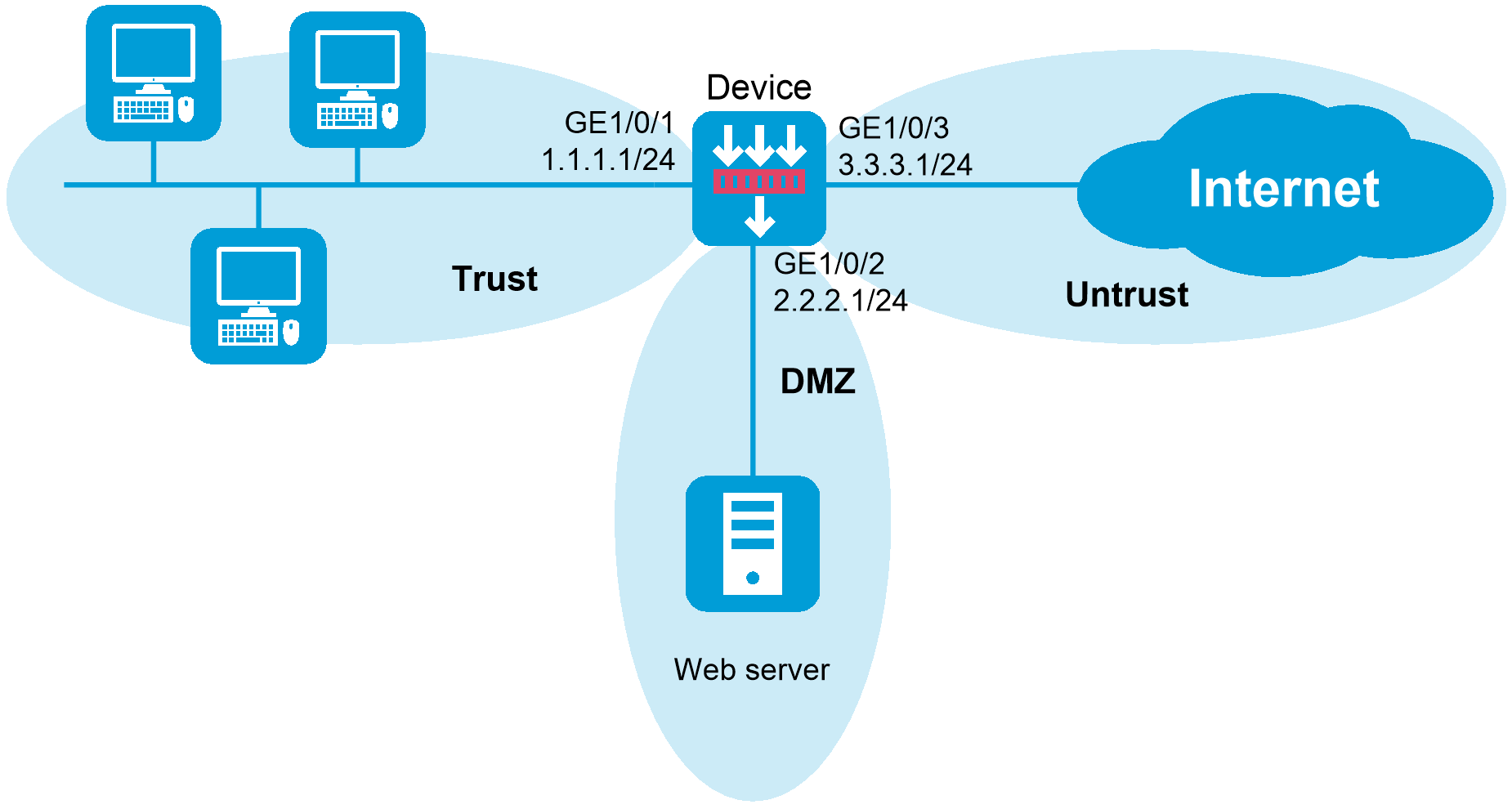
A DMZ isolates publicly reachable systems from internal devices.
- Use a DMZ for any VoIP system that must accept inbound internet traffic.
- Keep phones on the internal LAN or a dedicated voice VLAN.
- Only open the required SIP and RTP ports through the firewall.
Latency, Jitter, Packet Loss
Voice is sensitive to delay variation. Keep these in the green for stable calls.
| Metric | Excellent | Acceptable | Poor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latency | < 70 ms | 70-150 ms | > 150 ms |
| Jitter | < 10 ms | 10-30 ms | > 30 ms |
| Packet Loss | < 0.5% | 0.5-1% | > 1% |
What Is MTR?

MTR combines ping and traceroute so you can see loss and latency at every hop.
- Run it toward the provider when calls are choppy.
- Loss that starts mid-path is often ISP or transit related.
- Look for jitter spikes near the end of the path.
Ports 5060 and 5061
SIP is the signaling protocol that sets up calls. Media flows separately over RTP.
- 5060: SIP over UDP or TCP.
- 5061: SIP over TLS (encrypted signaling).
- RTP uses a provider-specific port range.
What Is SIP ALG?
SIP ALG is a router feature that edits SIP packets and often breaks VoIP.
- Best practice: disable SIP ALG for stability.
- Symptoms include one-way audio and dropped calls.
- Document the setting in your network checklist.
What Is WebRTC?
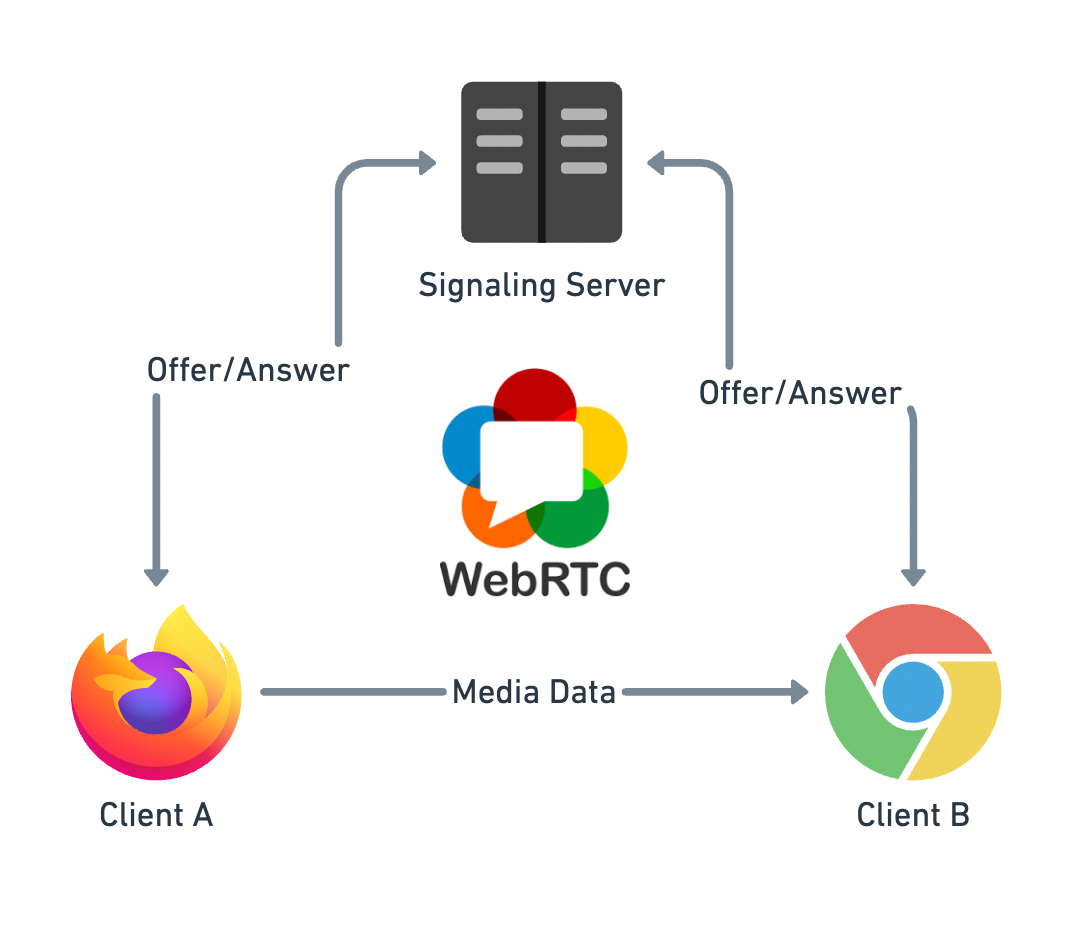
WebRTC delivers real-time voice and video directly in the browser without plugins.
- Used for softphones, web call widgets, and contact centers.
- Relies on ICE, STUN, and TURN for NAT traversal.
- Security is built-in with DTLS and SRTP.
What Are VoIP Trunks?
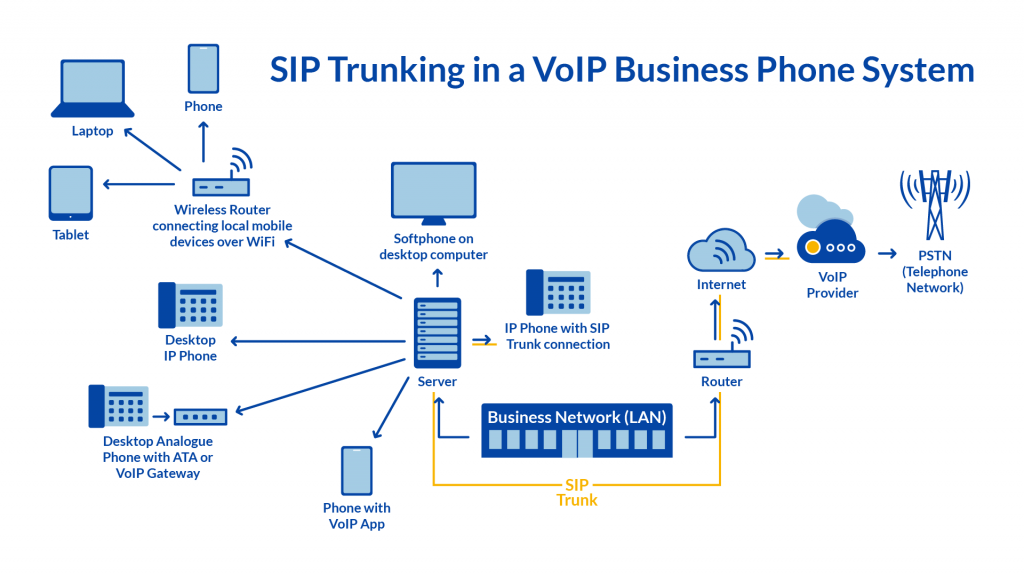
A SIP trunk is a shared connection between your phone system and the carrier.
- One trunk provides multiple simultaneous call paths.
- Scales without installing physical phone lines.
- Common for PBX-to-provider integrations.
STUN, TURN, ICE (NAT Traversal)
Remote users and WebRTC need NAT traversal to avoid one-way audio.
| Protocol | Purpose | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| STUN | Discover public IP/port | Most NAT scenarios |
| TURN | Relay media traffic | Restrictive firewalls |
| ICE | STUN first, TURN fallback | Default in WebRTC |
Wireshark & Packet Capture
Packet captures reveal SIP errors and RTP quality problems.
- Check Telephony → RTP → Stream Analysis for jitter and loss.
- Filter by SIP error codes to see failed calls.
Quick Troubleshooting Checklist
- Run MTR to the provider and look for loss or jitter.
- Verify QoS is enabled and voice is prioritized.
- Disable SIP ALG in the router or firewall.
- Confirm SIP + RTP ports are allowed.
- Test on wired Ethernet to rule out Wi-Fi jitter.
